Delving into Fiveable AP World Unit 5, we embark on a captivating journey through some of the most transformative events in human history. From the outbreak of World War I to the rise of nationalism and the Great Depression, this unit explores the complex interplay between global conflicts, revolutions, and economic transformations that shaped the modern world.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the causes and consequences of major historical events, analyze their impact on global diplomacy, and trace the evolution of cultural and intellectual trends that continue to influence our world today.
Global Conflicts and Diplomacy
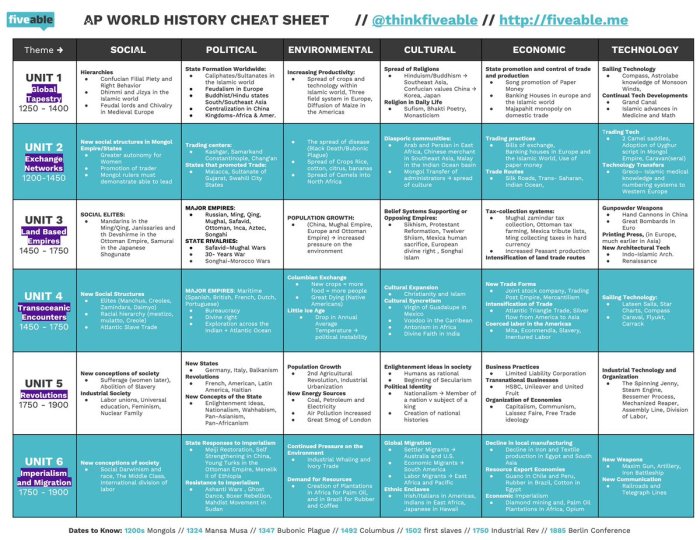
The 20th century was marked by major global conflicts that reshaped the world’s political, economic, and social landscapes. World War I, in particular, had a profound impact on global diplomacy and set the stage for future international relations.
Outbreak and Causes of World War I
The outbreak of World War I in 1914 was triggered by a complex web of factors, including:
-
-*Imperialism and Nationalism
The European powers were competing for colonies and influence around the world, leading to tensions and rivalries. Nationalism, a sense of pride and loyalty to one’s country, further fueled these conflicts.
-*Military Alliances
In Fiveable AP World Unit 5, you’ll explore the impact of European colonialism on the world. One notable example of this is the “pillars of adam and eve” rock formations , which were carved by European explorers in the 16th century.
These pillars serve as a reminder of the lasting legacy of colonialism and its impact on global history. As you delve deeper into Fiveable AP World Unit 5, you’ll uncover more fascinating examples of the consequences of European expansion.
A series of alliances between European powers created a system of entangling commitments. When one country mobilized for war, its allies were obligated to join, escalating tensions.
-*The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, by a Serbian nationalist on June 28, 1914, was the immediate catalyst for the outbreak of war.
Revolutions and Nationalism: Fiveable Ap World Unit 5
The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed a surge in revolutionary movements and the rise of nationalism, which profoundly shaped the course of global history. These forces had far-reaching consequences for international relations, decolonization, and the formation of modern nation-states.
The Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1917 was a pivotal event that led to the overthrow of the Tsarist regime and the establishment of the Soviet Union. The revolution had deep-rooted causes, including economic inequality, political repression, and the strains of World War I.
The consequences of the Russian Revolution were far-reaching. It inspired other socialist and communist revolutions around the world and led to the creation of a new superpower that would play a major role in international affairs throughout the 20th century.
The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
The 19th century saw a resurgence of nationalism in Europe. This sentiment was fueled by factors such as the rise of Romanticism, the spread of literacy, and the growth of industrialization.
Nationalism had a profound impact on international relations. It led to increased competition between European powers, as they sought to expand their territories and assert their national identities. It also contributed to the outbreak of World War I.
Nationalism and Decolonization
In the 20th century, nationalism played a crucial role in the decolonization process. As European empires weakened, nationalist movements emerged in colonies around the world.
These movements sought to achieve independence and self-determination. They often drew inspiration from the Russian Revolution and other socialist ideologies. The rise of nationalism in colonies ultimately led to the collapse of European empires and the creation of numerous new nation-states.
Economic Transformations
The early 20th century witnessed significant economic shifts that transformed global societies. The rise of industrialization and technological advancements spurred economic growth and urbanization, while the Great Depression brought unprecedented challenges and reshaped economic policies.
The Great Depression, Fiveable ap world unit 5
The Great Depression, which began in 1929, was a global economic crisis that devastated economies worldwide. Its causes were complex, including overproduction, stock market speculation, and international financial instability.
- Overproduction:Mass production led to a surplus of goods, causing prices to fall and businesses to struggle.
- Stock Market Speculation:Excessive buying and selling of stocks created an unsustainable bubble that burst in 1929.
- International Financial Instability:Global economic interdependence made the crisis spread rapidly, as countries defaulted on loans and withdrew gold from circulation.
The Great Depression had devastating consequences:
- Mass Unemployment:Millions lost their jobs, leading to widespread poverty and social unrest.
- Deflation:Falling prices made it difficult for businesses to repay debts and for consumers to afford goods.
- Political Instability:The crisis weakened governments and fueled the rise of extremist ideologies.
Cultural and Intellectual Trends
The 19th century witnessed a profound transformation in cultural and intellectual spheres, marked by the emergence of new ideas, artistic movements, and scientific discoveries that reshaped society and laid the groundwork for modern culture.
Romanticism
Romanticism, a literary and artistic movement that emphasized emotion, imagination, and the individual experience, emerged as a reaction to the Enlightenment’s emphasis on reason and logic. Romantic writers and artists sought to evoke powerful emotions through their works, exploring themes of love, nature, and the supernatural.
Realism
In contrast to Romanticism, Realism emerged as a literary and artistic movement that sought to depict life as it was, without idealization or exaggeration. Realist writers and artists aimed to capture the everyday lives and experiences of ordinary people, often focusing on social issues and the struggles of the working class.
Scientific Revolution
The 19th century witnessed a series of scientific breakthroughs that revolutionized our understanding of the natural world. From Darwin’s theory of evolution to the development of germ theory and the discovery of electricity, scientific discoveries had a profound impact on society, shaping our views on human origins, health, and technology.
Impact on Society and the Arts
These cultural and intellectual movements had a profound impact on society and the arts. Romanticism inspired a new appreciation for nature and the individual, while Realism brought attention to the social issues of the time. The Scientific Revolution transformed our understanding of the world and led to the development of new technologies that shaped modern life.
Examples
Examples of how these trends shaped modern culture include:
- Romantic literature and art influenced the development of modern poetry, music, and painting.
- Realist literature and art gave rise to social realism and naturalism in the 20th century.
- Scientific discoveries led to the development of modern medicine, transportation, and communication.
Popular Questions
What is the significance of Fiveable AP World Unit 5?
Fiveable AP World Unit 5 covers a crucial period in global history, examining the major conflicts, revolutions, and transformations that shaped the modern world.
What are the key topics covered in Fiveable AP World Unit 5?
The unit explores global conflicts such as World War I, revolutions like the Russian Revolution, economic transformations including the Great Depression, and cultural and intellectual trends that influenced society and the arts.
How can I effectively study for Fiveable AP World Unit 5?
Utilize a variety of resources such as textbooks, online materials, and practice questions. Create a study schedule, break down the content into manageable chunks, and engage in active recall techniques.

